Earth/Space Science Honors (#2001320)
This course is an equally rigorous science course with a lab component that satisfies part of the science graduation requirement (see below)
3 Credits Science • One of which must be Biology 1, two of which must be equally rigorous science courses • Two of the three required course credits must have a laboratory component • Industry Certifications that lead to college credit may substitute for up to one science credit (except for Biology 1) • An identified computer science** course may substitute for up to one science credit (except for Biology 1)
Principal Approved District Final - Counts for 10% of Final Course Grade
For Placement in Grade 9:
Completion of Grade 8 M/J Comprehensive Science 3 (with teacher recommendation)
For Placement Beyond Grade 10:
Students expressing a desire to follow an Environmental Pathway and have completed Biology.
For Placement in Grade 9:
Grade 8 M/J Comprehensive Science 3
For Placement Beyond Grade 10:
Biology 1 Honors
Gr 10 - Biology 1 Honors, Gr 11-12 - Any Equally Rigorous Science Honors Course (See Pathways Below)
Academic Pathways for Science
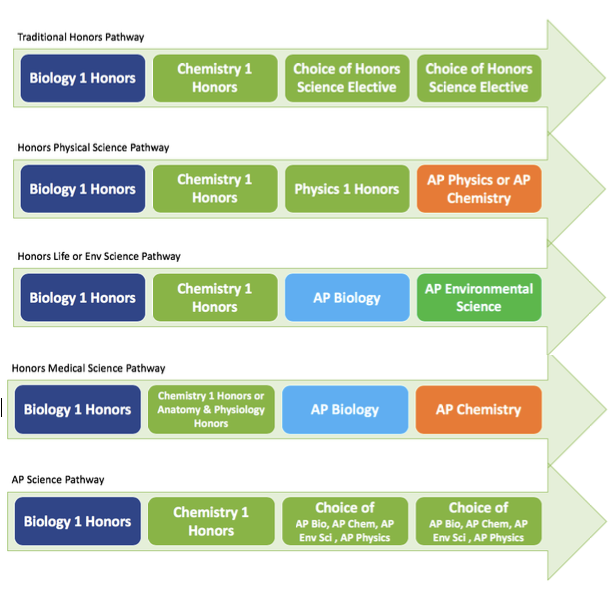
Honors Science Electives:
Anatomy & Physiology Honors, Chemistry 1 Honors, Earth & Space Science Honors, Environmental Science, Forensic Science, Genetics Honors, Marine Science, Marine Science 2 Honors, Physics Honors, Any Advanced Placement Science Course
Advanced Placement Science Courses:
AP Biology, AP Chemistry, AP Environmental Science, AP Research (at select schools), AP Physics
Access the Instructional Materials page to see approved instructional resources for this course.
Study the earth and its location in space through experiments and observation to discover a wide range of principles in the earth sciences. The term earth science is a broad one, encompassing geology, paleontology, plate tectonics, astronomy, meteorology, and oceanography. While the content focus of this course is consistent with the Earth/Space Science course, students will explore these concepts in greater depth. In general, the academic pace and rigor will be greatly increased for honors level course work.
Honors and Advanced Level Course Note: Advanced courses require a greater demand on students through increased academic rigor. Academic rigor is obtained through the application, analysis, evaluation, and creation of complex ideas that are often abstract and multi-faceted. Students are challenged to think and collaborate critically on the content they are learning. Honors level rigor will be achieved by increasing text complexity through text selection, focus on high-level qualitative measures, and complexity of task. Instruction will be structured to give students a deeper understanding of conceptual themes and organization within and across disciplines. Academic rigor is more than simply assigning to students a greater quantity of work.
Laboratory investigations that include the use of scientific inquiry, research, measurement, problem solving, laboratory apparatus and technologies, experimental procedures, and safety procedures are an integral part of this course. The National Science Teachers Association (NSTA) recommends that at the high school level, all students should be in the science lab or field, collecting data every week. School laboratory investigations (labs) are defined by the National Research Council (NRC) as an experience in the laboratory, classroom, or the field that provides students with opportunities to interact directly with natural phenomena or with data collected by others using tools, materials, data collection techniques, and models (NRC, 2006, p. 3). Laboratory investigations in the high school classroom should help all students develop a growing understanding of the complexity and ambiguity of empirical work, as well as the skills to calibrate and troubleshoot equipment used to make observations. Learners should understand measurement error; and have the skills to aggregate, interpret, and present the resulting data (National Research Council, 2006, p.77; NSTA, 2007).



